What is Hypothyroidism in children?
If the thyroid gland does not make enough hormones, we call it hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism in infants is a condition that affects about 1 in every 3,000 children. Types of hypothyroidism include:
Congenital: The child is born with the condition
Autoimmune: The immune system attacks the thyroid gland
Central: The thyroid does not get the correct signals from the hypothalamus or pituitary gland
Transient: A temporary condition
Post surgical: The thyroid gland was removed
How Does A Healthy Thyroid Work?
Thyroid hormone levels are tightly regulated to maintain health
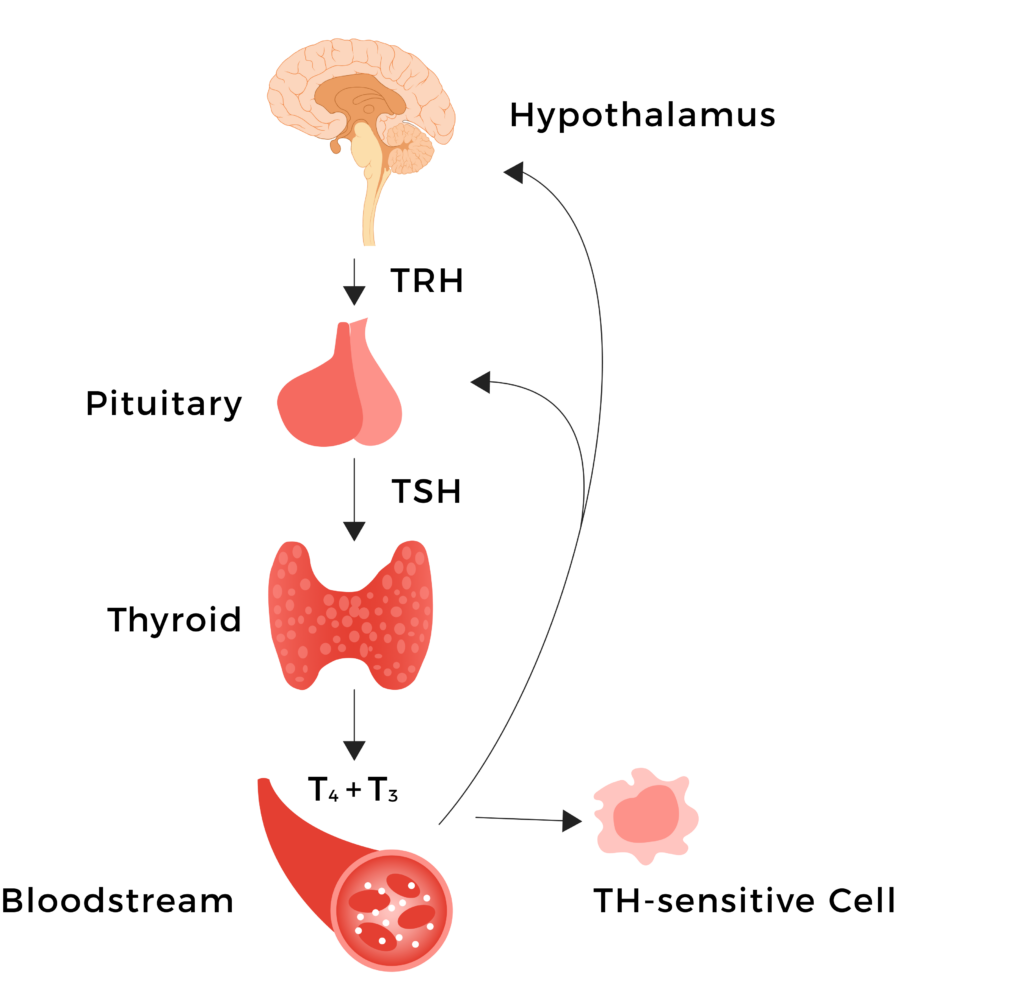
The Hypothalamus and pituitary signal the thyroid to produce T3 and T4. In turn, the hypothalamus and pituitary monitor T3 and T4 production to keep the system balanced.
- Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
- Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Thyroxine (T4)
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
 This adolescent has an enlarged thyroid gland, a condition known as goiter.
This adolescent has an enlarged thyroid gland, a condition known as goiter.
 Fatigue can also be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
Fatigue can also be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hypothyroidism In Kids?
Some infants with congenital hypothyroidism might not display symptoms, which is why screening for hypothyroidism is important and routine in the United States. If they do display symptoms, look for prolonged jaundice, decreased muscle tone, an enlarged tongue or umbilical hernia. Treatment of hypothyroidism in kids is essential as they are at high risk of permanent intellectual disability.
People whose thyroid function diminishes after birth, which we call acquired hypothyroidism, may experience goiter, anemia, menstrual irregularities, or delayed puberty.
Regardless of age, hypothyroidism may cause:
- Poor growth
- Decreased energy and fatigue
- Constipation
- Low red blood cell count
How Is Pediatric Hypothyroidism Diagnosed?
We diagnose pediatric hypothyroidism by analyzing the concentration of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine levels in the blood. Any child who consistently has TSH>7 mlU/L or a low thyroxine level will most likely need thyroid hormone replacement treatment. In short, a diagnosis of hypothyrodism hinges solely on lab results.
Why treat hypothyroidism in children?
Thyroid hormone is crucial for brain development in kids under 3 to prevent permanent intellectual disability. Even in older children, thyroid hormone is essential for normal growth and metabolism.
Parents should consider reaching out to a pediatric endocrinologist if they suspect their child may be experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism. It is crucial to seek medical attention from a pediatric endcrinologist who specializes in treating hypothyroidism in infants, children, and teens. Prompt intervention can help restore optimal thyroid hormone levels, ensuring healthy growth, development, and overall well-being for your child
Who treats hypothyroidism in children?
Pediatric Endocrinologists receive a total of six years of additional training after medical school. Their expertise in hormone imbalances uniquely qualifies them to treat hypothyroidism. Dr. McIver is a board certified online pediatric endocrinologist who has been practicing medicine since 2002 and has been treating hypothyroidism since 2007.
How Is Pediatric Hypothyroidism Treated?
We treat pediatric hypothyroidism by providing the body the hormones that the thyroid is not producing. Periodic lab work ensures that the prescription is accurate. Maintaining normal thyroid hormone levels will support normal growth and development.

 If the thyroid gland does not make enough hormones, we call it hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism in infants is a condition that affects about 1 in every 3,000 children.
If the thyroid gland does not make enough hormones, we call it hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism in infants is a condition that affects about 1 in every 3,000 children.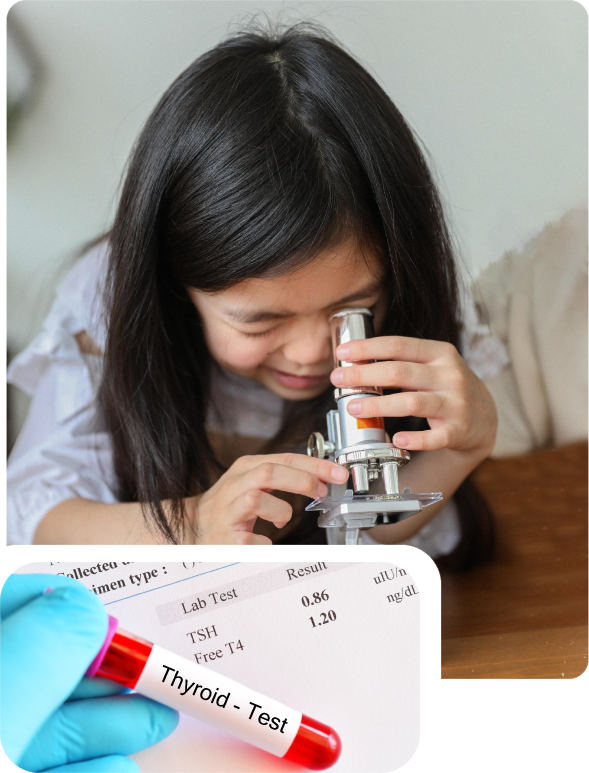  We diagnose pediatric hypothyroidism by analyzing the concentration of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine levels in the blood. Any child who consistently has TSH>7 mlU/L or a low thyroxine level will most likely need thyroid hormone replacement treatment. In short, a diagnosis of hypothyrodism hinges solely on lab results.
We diagnose pediatric hypothyroidism by analyzing the concentration of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine levels in the blood. Any child who consistently has TSH>7 mlU/L or a low thyroxine level will most likely need thyroid hormone replacement treatment. In short, a diagnosis of hypothyrodism hinges solely on lab results.


