Every parent wants their kid to be healthy, but it can be hard to spot the signs or notice when something is a little bit off with your child. Whether it is a common cold or something more serious, you want to be at the forefront of the problem to catch and treat the illness early. So, when it comes to hypothyroidism in kids, you need to be educated on what you’re looking for.
While it may seem daunting, arming yourself with knowledge is the first step in navigating this journey. We'll walk you through what hypothyroidism is, how to recognize its signs and symptoms, the different types, and most importantly, how to manage and support your child if they are diagnosed with this condition.
Let’s get started.
Is Hypothyroidism in Kids Common?
Before we dive deeper into the intricacies of pediatric hypothyroidism, let's address a pressing question: just how common is this condition among children? It's a question that often lingers in the minds of concerned parents, and rightfully so.
While autoimmune hypothyroidism is more frequently seen in adults, it's essential to recognize that children can also be affected. It is estimated that about 1-2% of children have hashimoto’s thyroid disease. There are also several other less common causes of hypothyroidism, some of which are discussed below.
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism, or CH, is a condition that a child is born with. The root causes of congenital hypothyroidism are typically related to abnormal development of the thyroid gland itself.
The exact prevalence varies across different regions and populations, but on a global scale, it is estimated that approximately 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 4,000 infants may be affected.

The most common cause is a failure of the thyroid gland to develop correctly during fetal development, known as thyroid dysgenesis. Less frequently, it can also result from defects in thyroid hormone synthesis or an inherited genetic condition that affects thyroid function.
While congenital hypothyroidism can present, on average, in 1 in 3000 infants, early detection through newborn screening programs has been instrumental in ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment as this leads to a good prognosis.
Acquired Hypothyroidism
On the other hand, acquired hypothyroidism is more likely to develop after the first year of life and can manifest at any point of childhood or adolescence. The leading cause of acquired hypothyroidism in children is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto's thyroiditis, wherein the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the thyroid gland.
Other potential causes of acquired hypothyroidism in children may include certain medications, radiation therapy, or surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). Additionally, iodine deficiency, though rare in many developed countries due to dietary supplementation, can lead to acquired hypothyroidism if untreated.
What Does the Thyroid Do?
Before delving into the specifics of thyroid problems and their impact on children, it's crucial to grasp the thyroid's fundamental role in the body.
The thyroid gland, located in the front of the neck, is a small but mighty organ with a big responsibility: it regulates the body's metabolism. It does so by producing two critical hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which play a central role in influencing how cells use energy and in the overall functioning of the body.
In growing children, the thyroid is especially essential. Thyroid hormones are like the body's metabolic conductors, orchestrating a symphony of processes that support physical and mental growth. They impact everything from the development of the brain and nervous system to the growth of bones and muscles.
Potential Effects of Thyroid Problems on Child Development
Thyroid problems, particularly hypothyroidism, can cast a shadow over a child's life, affecting various aspects of their physical and cognitive development. Let's take a closer look at the potential consequences.
Slower Growth
One of the most noticeable effects of untreated hypothyroidism in children is slower growth. The thyroid hormones are essential for the growth and development of bones and muscles. When these hormones are deficient, children may exhibit stunted growth compared to their peers.
Parents and caregivers might notice that their child isn't reaching typical height and weight milestones or that they are consistently shorter than other kids their age.
Lack of Activity
Fatigue and lethargy are common symptoms of hypothyroidism in children. As a result, affected kids may lack the energy and motivation to participate in physical activities and play like other children. This reduced activity can not only hinder their physical development but may also affect their social interactions and overall quality of life.

Poor School Performance
Thyroid hormones are crucial for brain development and cognitive function. When a child's thyroid is underactive, it can lead to memory problems, and a possible decline in school performance. Children with untreated hypothyroidism may struggle with academic tasks, leading to frustration and a decline in self-esteem.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism in Kids
Here are some common signs of hypothyroidism in kids. It's important to remember that not all children with hypothyroidism will experience every symptom, and the severity of symptoms can vary.
- Fatigue and Lethargy
- Weight Gain
- Dry Skin
- Slowed Growth
- Constipation
- Cold Intolerance
- Puffy Face
- Hoarse Voice
- Slow Heart Rate
- Hair Changes
- Delayed Puberty (in adolescents)
- Memory and Concentration Issues
- Mood Changes
- Muscle Weakness
- Joint Pain
- Menstrual Irregularities (in adolescent girls)
If you notice any of these signs in your child, especially if they persist or worsen over time, it's advisable to consult a pediatric endocrinologist for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis.
Types of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism in kids and adults can form in different ways, and understanding the differences is essential for proper diagnosis and management. Let’s go over the different types.
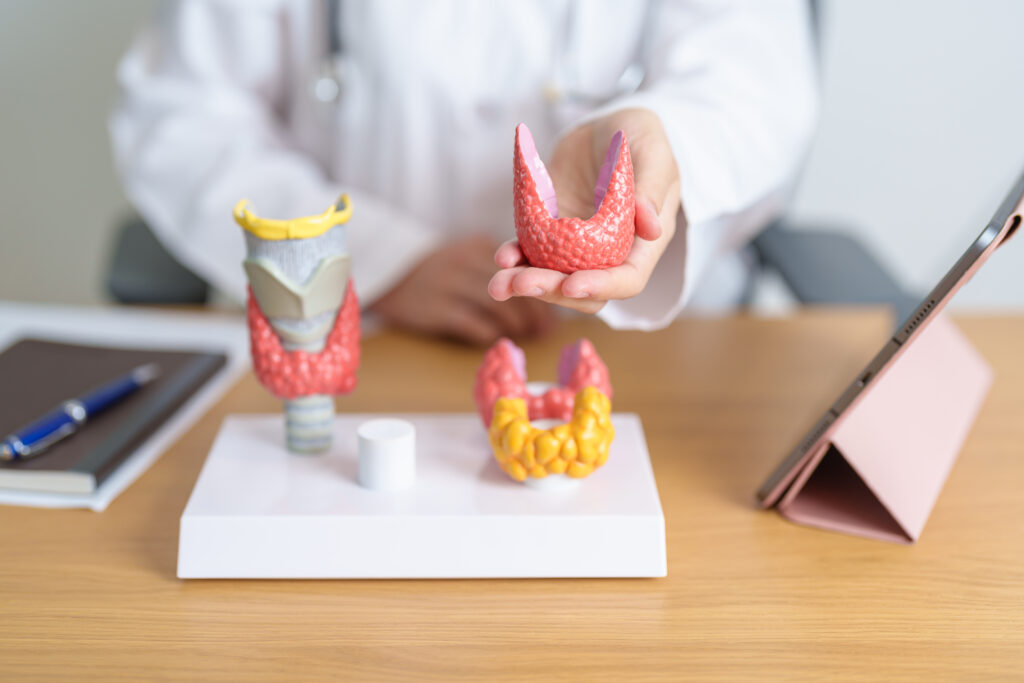
Autoimmune Hypothyroidism
Autoimmune hypothyroidism, also known as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, is the most common cause of acquired hypothyroidism in kids. It occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage.
Causes: The exact cause of autoimmune hypothyroidism is not fully understood, but it is believed to have a genetic disposition. As having a family history of autoimmune thyroid disorders can increase a child's risk.
Symptoms: Symptoms are similar to those of other forms of hypothyroidism and may include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and poor school performance.
Iatrogenic Hypothyroidism
Iatrogenic hypothyroidism refers to hypothyroidism that is induced by medical treatment, often involving the use of certain medications or surgical procedures.
Causes: This type of hypothyroidism can be caused by the surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) or as a side effect of certain medications, such as those used to treat hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms: Iatrogenic hypothyroidism presents with typical hypothyroid symptoms and may require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy in particular, those who had their thyroid gland removed.
Central Hypothyroidism
Central hypothyroidism, also known as secondary or tertiary hypothyroidism, is a less common form of hypothyroidism in children. It arises when there is an issue with the pituitary gland or the hypothalamus in the brain, which are responsible for regulating thyroid hormone production.
Causes: Central hypothyroidism can be congenital (present from birth) or acquired due to tumors, radiation, or other damage to the pituitary or hypothalamus.
Symptoms: Symptoms may vary and can include growth delay, delayed puberty, and fatigue. Because it involves dysfunction in the brain's signaling, the presentation may differ from typical hypothyroidism.
Each type of hypothyroidism in children requires a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment. In all cases, early detection and management are crucial to mitigating the impact on a child's growth, development, and overall well-being.
Treating Hypothyroidism in Kids
Hormone replacement therapy is the primary treatment for hypothyroidism in kids. Since the thyroid gland isn't producing sufficient thyroid hormones, synthetic thyroid hormone medication, such as levothyroxine, is prescribed. The dosage is carefully adjusted aiming to restore thyroid hormone levels to normal.
This treatment is usually lifelong, and regular monitoring through blood tests is essential to ensure the child receives the correct dose. With prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, children with hypothyroidism can lead healthy, fulfilling lives, with their growth, development, and overall health fully supported by maintaining optimal thyroid hormone levels.
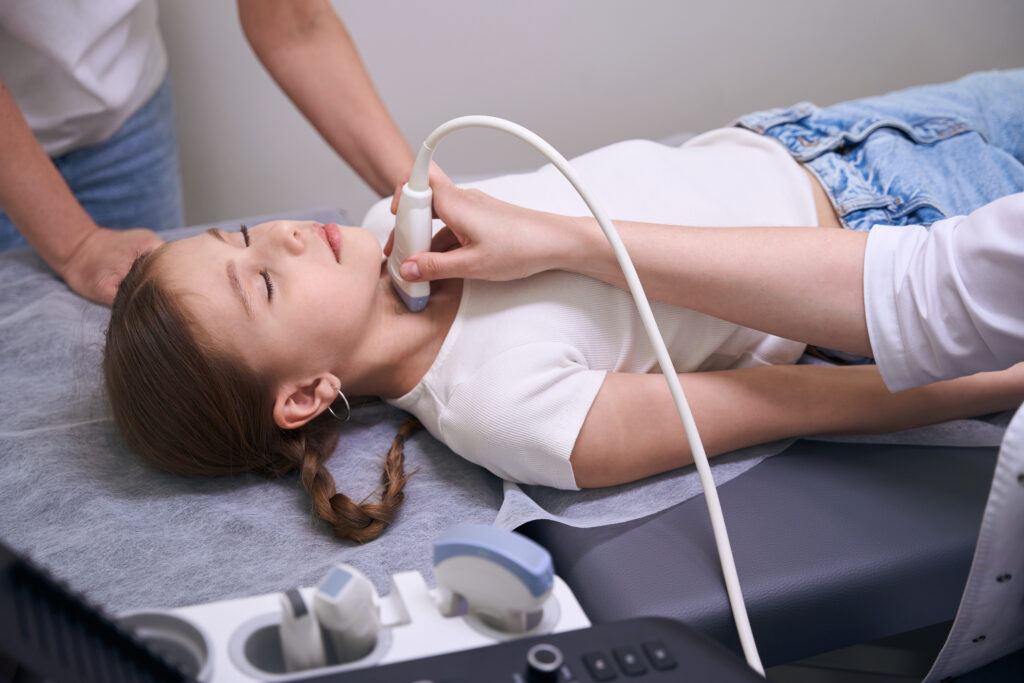
Give Your Child the Treatment They Deserve
Now that we’ve discussed the signs and symptoms that parents should be vigilant about, it should be easy to understand the importance of early detection and intervention. Remember, if you suspect your child may be experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism or if you have questions and concerns, you don't have to navigate this journey alone. Expert guidance can make all the difference in your child's health and well-being, and pediatric endocrinologist Dr. McIver is here to help.

